
The LASAPE synthesizes methyl biodiesel by heterogeneous catalysis, using abundant raw materials in Brazil, such as crude soybean oils recovered (frying) and soya bean lecithins.
Rudolf Diesel developed and patented the engine powered by vegetable oil in the late nineteenth century. A major problem of the invention was to obtain seeds with a high production cost. The abundance of petroleum in the early twentieth century and the low cost of its oil refining made vegetable oils be replaced by petroleum refined oil, which was called "diesel oil".
However fossil fuels have a number of disadvantages, and thus creating the possibility to develope renewable energy sources.
- Major polluters of the environment;
- It is not a renewable source of energy;
- The growing consumption, the geographic concentration of deposits and the price volatility.
Advantages of biodiesel compared with fossil fuel:
- It is derived from renewable raw materials naturally occurring;
- It is biodegradable;
- Reduction in emissions of exhaust gases;
- It has a high flash point.
Quality Biodiesel: ANP Resolution No. 14 of 11/05/2012
- Contaminants from the raw material: phosphorus, sulfur, calcium, magnesium;
- Evaluation of the production process: free and total glycerin; carbon residue; ester content; flash point; methanol and ethanol;
- Inherent properties to Molecular structures: density, kinematic at 40 ° C, iodine number, cetane number and viscosity pour point.
- Inherent properties in the process of storage: Oxidation stability at 110 ° C, acid number, water and sediments.
Soybean oil as raw materials for methyl biodiesel synthesis
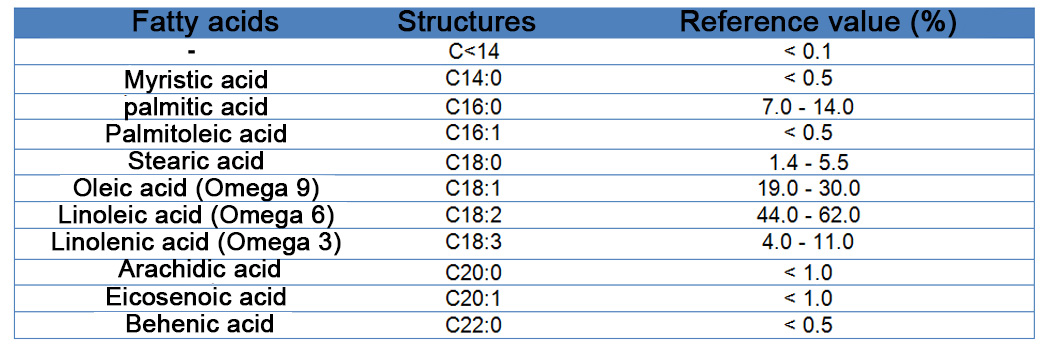
Reference Values: RDC No. 482 of 23/09/1999, the National Agency of Sanitary Surveillance - ANVISA/Brazil.
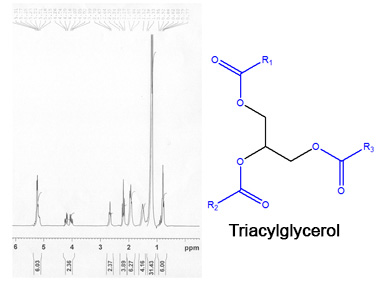
Characteristics of vegetable oils: use "in natura" as fuel
- Triglycerides liquid at room temperature;
- High viscosity and low volatility;
- Incomplete combustion;
- Plugging in the injection systems and clogging of oil filters;
- Formation of carbon deposits in the injection systems;
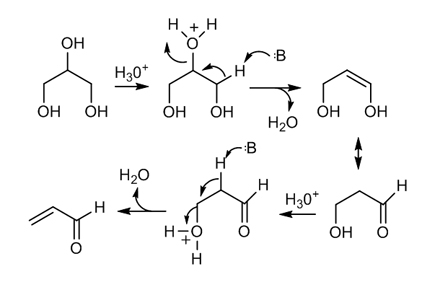
- The thermal decomposition of glycerol leads to the formation of acrolein. (Highly poisonous; causes irritation to membranes; Highly flammable liquid and vapor).
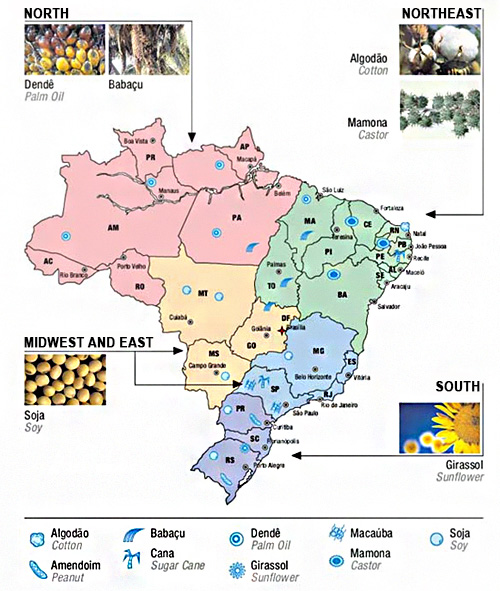
Brazilian has a major potential for vegetable fuels production.
Transesterification reaction
Chemical reaction between an ester and an alcohol which results in a new ester and an alcohol.
Examples:
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET);
- Alkyd resins in oil inks composition;
- Fatty esters are inputs for oleochemical derivatives;
- In the energy sector, the biodiesel.
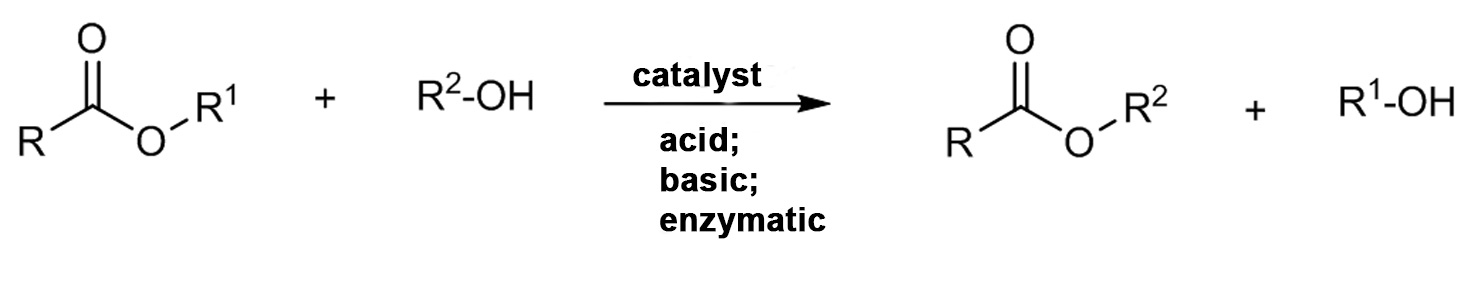
Transesterification of vegetable oils
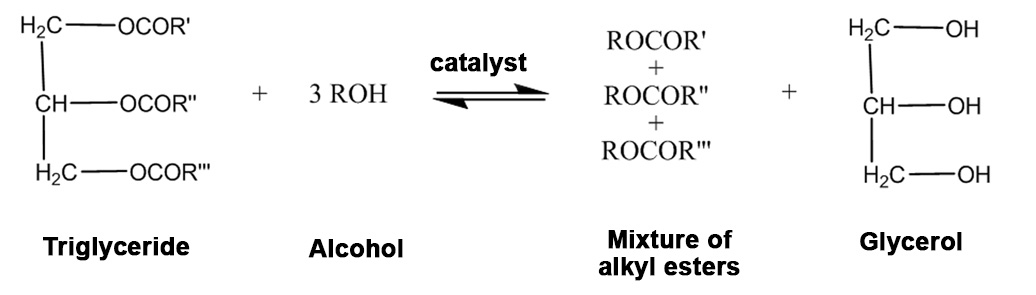
Homogeneous or heterogeneous catalysts: acidic, basic or enzymatic
Basic homogeneous catalysis: hydroxides, carbonates and alkoxides of Na and K;
- Advantages: it is very fast, with excellent yields;
- Disadvantages: sensitivity to the presence of water and free fatty acids, saponification.
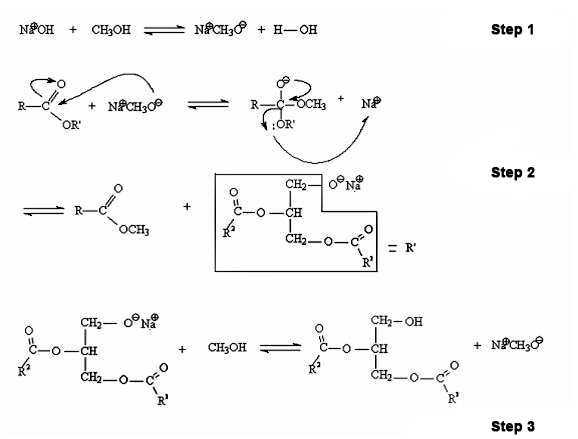
Homogeneous acid catalysis: HCl, H2SO4
- Advantages: does not require free water raw materials and free fatty acids; separation of glycerin;
- Disadvantages: is slow removal of cat, isomerization of double and polymerization;
Enzymatic catalysts: lipases
- Advantages: low sensitivity to the presence of water; recovery of the catalyst; separation of biodiesel; environmentally more attractive;
- Disadvantages: high cost and the difficulties related to process control;
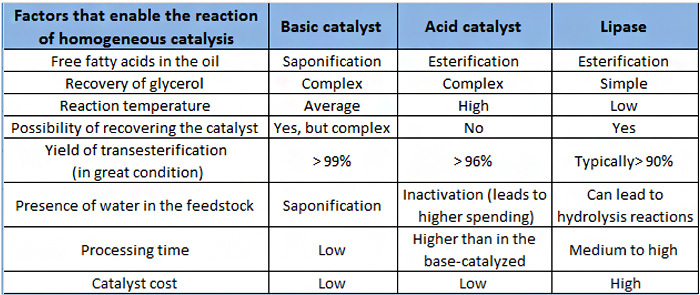
Heterogeneous catalysts:
- Advantages: increase the sustainability of the production process, facilitates purification, recycling of solid catalyst throughout his lifespan, minimizes the generation of effluent and facilitates the recovery and purification of glycerin
- Basics: CaO, CaCO3, CaO/Al2O3, KOH / MgO
- Acids: Zirconia Alumina with tungsten, sulfated tin oxide, sulfated zirconia on alumina.
See Technological Consultancy for more information.